Risk Management
PT Alamtri Minerals Indonesia Tbk ("AMI" or "the Company") and its subsidiaries are exposed to various internal and external risks, which must be identified and then managed effectively, i.e. in a structured, systematic and consistent manner, with the involvement and support of all hierarchical levels of the organization. Effective risk management must be implemented in every operational activity, especially in the decision-making process, in order to ensure the sustainability of the company’s business and contribute to increasing shareholder value through sound business growth.
Risk Management Policy
The risk management policies at AMI are designed to involve and integrate all hierarchical levels of the organization, within which the company has formed a Risk Management Sponsor Committee and Risk Management Unit, as well as appointing Risk Champions for each subsidiary. Risk Champions are tasked with identifying the risks faced by their company (critical, high, moderate, or low levels), developing the strategies and action plans needed to handle the identified risks, and then proposing the strategies to the director of the associated subsidiary. Risk Champions also communicate their risk management strategies with the risk management team at the parent company and receive management directions based on the risk management strategies implemented across the companies within AMI by attending risk forums held every month.
Risk Management Standard
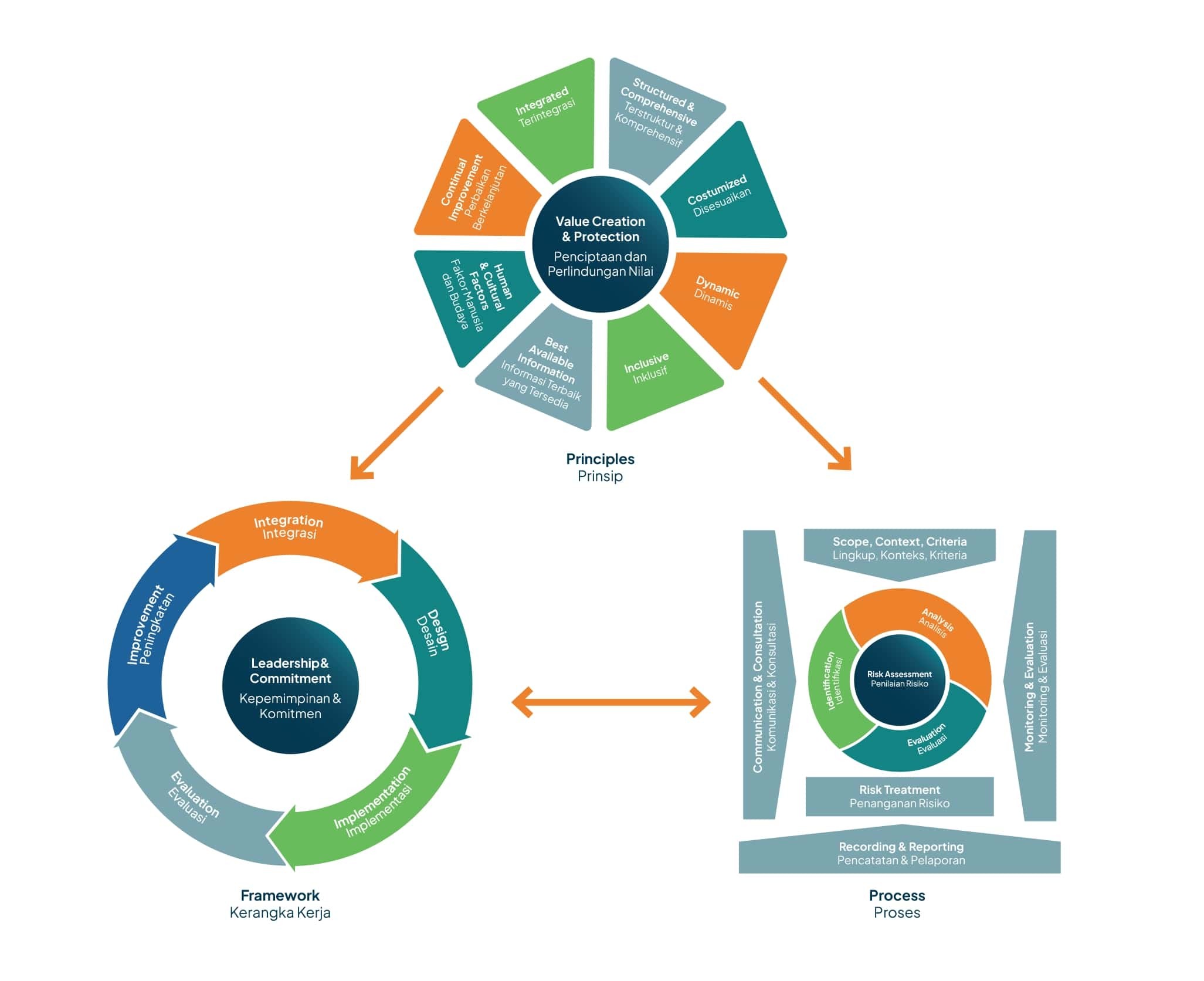
AMI has adopted ISO 31000:2018 – Risk Management Guideline, consisting of 3 (three) main components:
- Risk management principle, with these characteristics:
- Integrated.
- Structured & comprehensive.
- Adjusted.
- Inclusive.
- Dynamic.
- Best available information.
- Human and cultural factors.
- Continuous improvement.
- Risk management framework, consisting of:
- Leadership and commitment:
- Issuing risk management statement or policy.
- Ensuring resource availability.
- Determining authority, responsibility, and accountability.
- Adjusting and implementing all components of the framework
- Integration of risk management into the entire business processes, through:
- Planning, implementation, and achievement of company targets and goals.
- Business process and project management.
- HSE management.
- Crisis management.
- Internal audit.
- Design, with the philosophy “make it clear, make it simple”, risk management is designed to consist of three levels: strategic, tactical, and operational.
- Implementation, risk management is implemented by top-down and bottom-up approaches to ensure the integration of the parent company and subsidiaries’ risk management using ORMP approach (objective, risk, mitigation and planning).
- Evaluation, the management determines the risk management targets, regularly measures the progress through maturity level assessment and risk culture survey, reviews the policy and technical guideline, and monitors the effectiveness of risk management framework and process.
- Risk management improvement, the evaluation outcome is followed up to improve risk management continuously.
- Leadership and commitment:
- Risk management process, consisting of:
- Communication and consultation.
- Determination of scope, context, and criteria.
- Risk identification, analysis, and evaluation.
- Risk treatment.
- Risk monitoring and review.
- Recording and reporting.
Three Lines of Defense Model
The three lines of defense model is used to ensure checks and balances. This model consists of:
- First line: consisting of all subsidiaries responsible for managing risks.
- Second line: consisting of all corporate functions excluding Internal Audit Department, responsible for providing risk expertise, support, monitoring, and evaluation, including determining the policy, standard, technical guidelines, and other risk management tools.
- Third line: Internal Audit Department, responsible for providing independent and objective assurance on control (governance, risk management, and internal control). Additional assurance may also be obtained from external parties such as external auditor.
To ensure that risk management strategies and policies are properly implemented by the three lines for risk-based strategic decision making, the company has supervisory organs consisting of the Board of Directors, the Board of Commissioners, and Risk Management Sponsor Committee to oversee the supervisory role. The first line and second line report to the supervisory organs, while the third line provides assurances to the supervisory organs on the risk management and control effectiveness. The explanation on the supervisory organs is presented below:
- The Board of Commissioners is responsible for monitoring how the company accounts for risk aspects in drawing up strategies, providing guidelines on risk appetite, and delegating the tasks to the Audit Committee.
- The Board of Directors determines the risk appetite in all categories, takes responsibility on risk management effectiveness, and ensures that all business strategies and decisions are made by considering the identified risks. The Board of Directors receives risk reports regularly and communicates the risk profiles with the Board of Commissioners.
- Risk Management Sponsor Committee supports the Board of Directors in providing directions and recommendations, and monitoring risk management. This committee also ensures that the risk programs are aligned with the company’s strategies, resources are sufficient, and mitigation measures run effectively, and regularly assesses risk performance and policies.
Crisis Management
In 2024, AMI enhanced the preventive actions by referring to the outcomes of the previous drills and groupwide risk analysis to identify catastrophic risks to be focused on in the subsequent simulations. This step aims to make all operational units more ready to update and adjust each crisis plan with the current risk contexts.